Object.assignとは
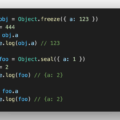
プロパティの値をターゲットオブジェクトへコピーできる。
const obj1 = {
a: 1,
b: 2
};
const obj2 = Object.assign({c: 3, d: 4}, obj1);
console.log(obj2);
// => {c: 3, d: 4, a: 1, b: 2}
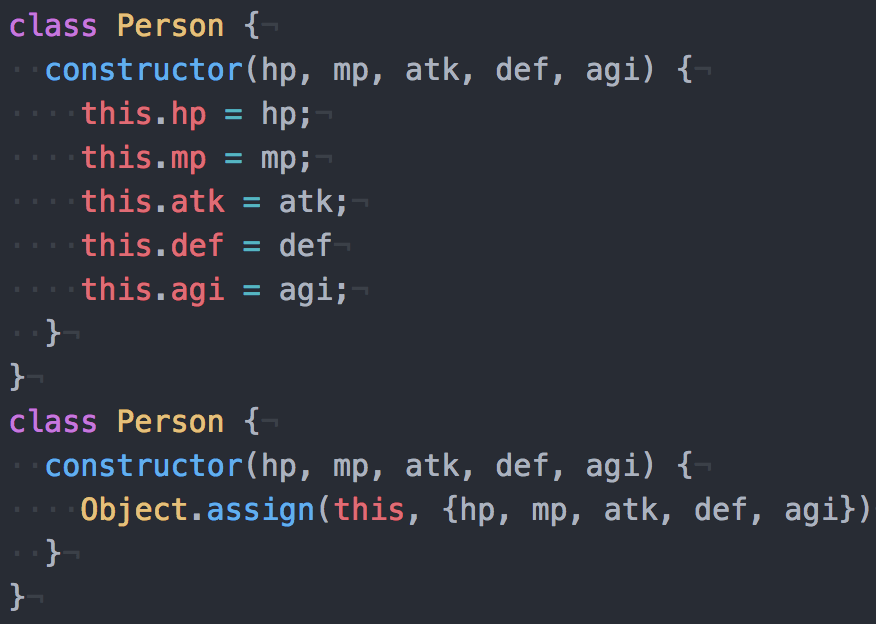
Classのconstructorでthis.foo = fooという書き方をする人が多いが、Object.assignを使用すれば第1引数にthisを入れて、第2引数にfooを入れればコード量が少なく可読性も高い。
// よくある書き方
class Person {
constructor(hp, mp, atk, def, agi) {
this.hp = hp;
this.mp = mp;
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def
this.agi = agi;
}
}
// Object.assignでの書き方
class Person {
constructor(hp, mp, atk, def, agi) {
Object.assign(this, {hp, mp, atk, def, agi})
}
}
const goblin = new Person(5, 4, 3, 2, 1);
console.log(goblin.atk); // => 3
見ての通りObject.assignはconstructorと「hp, mp, atk, def, agi」の部分が同じなので、そのままコピペできて保守性も高い。
Object.assignはBabelでは変換されないのでWebサイトで使用する場合はPolyfillが必須。
Object.assign() - JavaScript | MDN